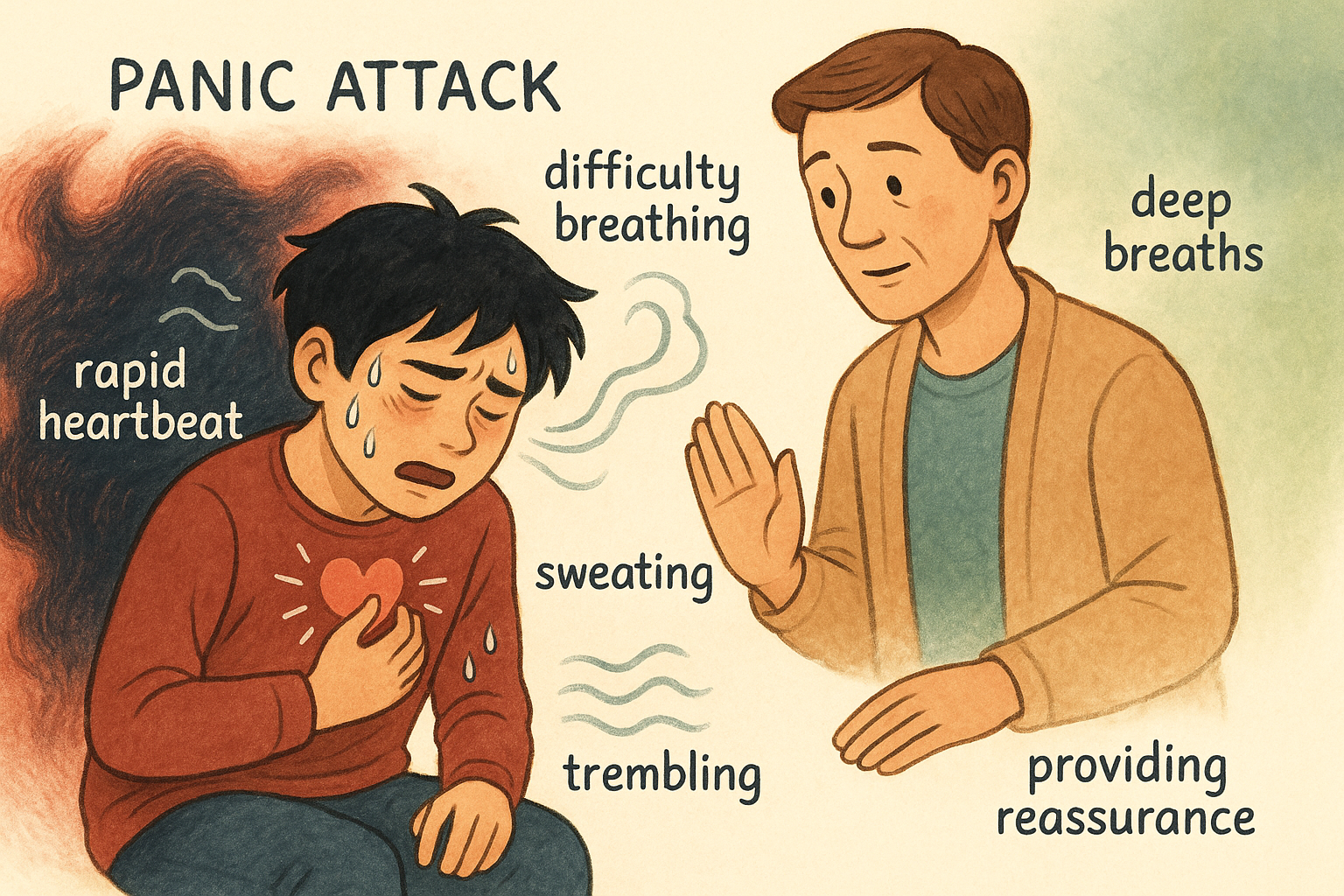
Academic anxiety significantly impacts many teenagers, creating a complex relationship between school performance and mental health. When anxiety interferes with learning, it can create a cycle where poor academic performance increases anxiety, which further impairs academic functioning. Understanding this relationship and implementing targeted strategies can help anxious teens achieve academic success while managing their mental health.
Understanding Academic Anxiety in Teens
Academic anxiety encompasses various fears and worries related to school performance, including test anxiety, fear of failure, perfectionism, and social anxiety around academic situations. This type of anxiety can manifest in different ways and significantly impact a teen’s ability to learn, perform, and engage in their education.
Common Forms of Academic Anxiety:
- Test and evaluation anxiety
- Performance anxiety during presentations
- Fear of asking questions or participating in class
- Procrastination due to perfectionism
- Social anxiety in group learning situations
- General worry about grades and academic achievement
How Anxiety Affects Learning and Performance
Cognitive Impact: Anxiety can impair working memory, concentration, and information processing, making it difficult for teens to absorb and retain new information effectively.
Physical Symptoms: Anxiety-related physical symptoms like headaches, stomachaches, and fatigue can interfere with school attendance and classroom focus.
Avoidance Behaviors: Anxious teens may avoid challenging assignments, skip classes, or procrastinate on important tasks to avoid anxiety-provoking situations.
Sleep Disruption: Anxiety about school can interfere with sleep, which further impairs cognitive function and academic performance.
Social Withdrawal: Academic anxiety can lead to isolation from peers and teachers, reducing opportunities for collaborative learning and support.
Test Anxiety: Specific Strategies for Success
Preparation Techniques:
- Create structured study schedules to reduce last-minute cramming
- Use active learning techniques like practice tests and summarization
- Form study groups to share knowledge and reduce isolation
- Visit teachers during office hours for clarification and support
Test-Taking Strategies:
- Arrive early to settle in and reduce rushing
- Practice relaxation techniques before and during tests
- Read instructions carefully and plan time allocation
- Start with easier questions to build confidence
- Use positive self-talk and affirmations
Physical Preparation:
- Get adequate sleep before test days
- Eat a balanced breakfast to maintain energy and focus
- Practice deep breathing exercises
- Engage in light physical activity to reduce tension
Managing Perfectionism in Academic Settings
Redefine Success: Help teens understand that learning involves making mistakes and that perfect performance isn’t always necessary or realistic.
Set Realistic Goals: Encourage teens to set achievable, specific goals rather than vague aspirations for perfection.
Time Management: Teach teens to set time limits for assignments to prevent endless revision and perfectionist paralysis.
Celebrate Progress: Focus on improvement and effort rather than only recognizing perfect outcomes.
Learn from Mistakes: Encourage teens to view errors as learning opportunities rather than personal failures.
Study Strategies for Anxious Teens
Break Down Large Tasks:
- Divide big projects into smaller, manageable steps
- Create timelines with specific milestones
- Celebrate completion of each step
- Use visual organizers to track progress
Create Anxiety-Friendly Study Environments:
- Find quiet, comfortable spaces with minimal distractions
- Use natural lighting when possible
- Keep study areas organized and clutter-free
- Have anxiety management tools readily available
Active Learning Techniques:
- Use flashcards and spaced repetition
- Create mind maps and visual representations
- Teach concepts to others or explain them aloud
- Practice retrieval through self-testing
Communication with Teachers and School Staff
Self-Advocacy Skills: Teach teens how to communicate their needs and challenges to teachers and counselors appropriately.
Building Relationships: Encourage teens to develop positive relationships with teachers who can provide support and understanding.
Seeking Help Early: Encourage teens to ask for help before problems become overwhelming, rather than waiting until they’re struggling significantly.
Understanding Accommodations: If appropriate, work with school staff to identify accommodations that can support academic success.
Academic Accommodations for Anxious Teens
When anxiety significantly impacts academic performance, formal or informal accommodations may be helpful:
Testing Accommodations:
- Extended time for tests and assignments
- Quiet testing environments
- Alternative testing formats
- Breaks during long exams
Classroom Accommodations:
- Preferential seating near exits or away from distractions
- Modified participation requirements
- Alternative presentation formats
- Advance notice of changes in routine
Assignment Modifications:
- Alternative formats for demonstrating knowledge
- Modified deadlines when appropriate
- Breaking large assignments into smaller parts
- Flexible attendance policies for mental health needs
Building Academic Confidence
Focus on Strengths: Help teens identify and build upon their academic strengths and interests.
Set Incremental Goals: Create achievable short-term goals that build toward larger academic objectives.
Track Progress: Keep records of improvements and achievements to build confidence over time.
Develop Growth Mindset: Encourage teens to view challenges as opportunities to learn and grow rather than threats to their self-worth.
Celebrate Effort: Recognize and praise the process and effort rather than just outcomes.
Managing Academic Stress and Workload
Time Management Skills:
- Use planners and calendars to organize assignments and deadlines
- Prioritize tasks based on importance and urgency
- Build in buffer time for unexpected challenges
- Schedule regular breaks and downtime
Workload Balance:
- Avoid overcommitting to extracurricular activities
- Learn to say no to additional responsibilities when overwhelmed
- Maintain balance between academic and social activities
- Recognize signs of burnout and take action early
Social Aspects of Academic Performance
Peer Support: Encourage participation in study groups and peer tutoring programs that provide both academic and social support.
Collaborative Learning: Help teens find ways to engage in group projects and collaborative learning that feel manageable.
Reducing Competition: Focus on personal progress rather than comparison with other students.
Building Social Skills: Develop communication and collaboration skills that support academic success.
Technology Tools for Academic Success
Organization Apps: Use digital planners, reminder systems, and organization tools to manage academic responsibilities.
Study Apps: Utilize flashcard apps, note-taking tools, and educational resources that support learning.
Anxiety Management Apps: Incorporate mindfulness and relaxation apps into study routines.
Communication Tools: Use appropriate technology to communicate with teachers and classmates about academic matters.
Parent and Family Support for Academic Success
Create Supportive Home Environment:
- Provide quiet, organized spaces for homework and study
- Maintain consistent routines that support academic success
- Show interest in school activities without being overwhelming
- Celebrate effort and progress, not just grades
Communication with School:
- Maintain regular contact with teachers and counselors
- Attend school meetings and events when possible
- Advocate for your teen’s needs while encouraging self-advocacy
- Support but don’t override your teen’s communication with school staff
Long-Term Academic Planning
College and Career Preparation: Help anxious teens develop realistic plans for their future that account for their mental health needs and strengths.
Skill Development: Focus on building life skills and coping strategies that will support long-term academic and professional success.
Mental Health Maintenance: Ensure that academic planning includes consideration of mental health support and self-care.
Flexibility: Maintain flexibility in academic and career plans to accommodate changing needs and circumstances.
When to Seek Additional Support
Consider professional academic or mental health support if:
- Anxiety significantly impairs daily academic functioning
- School avoidance becomes frequent or persistent
- Academic performance declines significantly despite effort
- Anxiety about school impacts other areas of life
- Teen expresses feelings of hopelessness about school
Building Resilience for Academic Challenges
Remember that academic success for anxious teens isn’t just about grades – it’s about developing the skills, confidence, and resilience needed for lifelong learning and growth. With proper support and strategies, anxious teens can achieve academic success while maintaining their mental health.
For comprehensive support in managing teen anxiety and academic challenges, visit StillNest Health. Our guides specialize in helping teens develop effective strategies for academic success while managing anxiety.
The goal is to help teens develop sustainable approaches to academic achievement that support both their educational goals and their mental health needs.
Discover more resources for teen anxiety and academic support at StillNest Health.
Related Help Guide Downloads
-
Study Smarter, Not Harder: Transform Teen Academic Performance with Science-Backed Methods Digital Guide
Original price was: $34.00.$17.00Current price is: $17.00. -
Academic Edge Bundle: Teen Sleep Success, Study Smarter, Screen Smart, Mindful Teen.
Original price was: $68.00.$39.00Current price is: $39.00.